The History of the Top Six Banks in Canada
Retail Banking is a financial business that provides a wide range of personal services, including offering savings and checking accounts, bill paying services, as well as debit and credit cards. Through retail banking, consumers may also obtain mortgages and personal loans.
Although retail banking is for the most part mass-market driven, many retail banking products may also extend to small and medium sized businesses. Today, several retail banking services are available electronically through Automated Teller Machines (ATMs), or online banking. (Raghuwanshi, 2012)
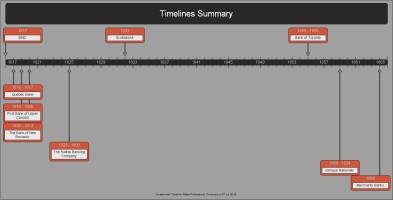
In the British North American Provinces, early banking activities can be traced to 1792, when English firms and Montreal merchants founded the Canada Banking Company; this was one of the first attempts to establish formal banking services in colonial Canada. However, it was only until 1817 with the opening of The Bank of Montreal in the Province of Lower Canada; that an organization would have the appropriate mechanism in place to support continuing banking services.
With a capital of about £250,000 Halifax currency, The Bank of Montreal initiated operations under the article of association until the provincial charter was granted in 1882 (Breckenridge, 1910). From this moment forward, other institutions would follow BMO’s path, and their success and failures contributed to the establishment of what currently is recognized as the soundest banking system in the world (Department of Finance Canada, 2013). The next two hundred years of Canada retail banking history can be summarized as follows:
- In 1818, The Quebec Bank was established in the province of Lower Canada, and it remained in business until 1917 when was absorbed by the Royal Bank of Canada.
- RBC was founded in Halifax, in 1864 under the name of Merchants Bank. Today RBC is the largest bank in Canada in terms of assets and market penetration (Office of the Superintendent of Financial Institutions Canada, 2013).
- 1819, The First Bank of Upper Canada Province initiated operations and was charted in 1821 just after the Bank of Kingston in 1819. It was the major bank in Ontario until it collapsed in 1866 (Baskerville, 2006).
- 1820, The Bank of New Brunswick was established and merged with the Bank of Nova Scotia 1913. Scotiabank was founded in 1832 in Halifax and currently has a strong presence in Latin American and the Caribbean (Scotiabank, 2010).
- 1825, the Halifax Banking Company, the first bank in Nova Scotia, eventually would merge with the Canadian Bank of Commerce in 1903, which then merged in 1961 with the Imperial Bank of Canada and became CIBC, The Canadian Imperial Bank of Commerce (Canadian Imperial Bank of Commerce, 2013).
- 1855, the Bank of Toronto was founded in Toronto and operated until merging with The Dominion Bank in 1955 becoming the Toronto-Dominion Bank (TD Bank, n.d.). Today, TD is the most valuable brand with a value of $9.69 billion (Interbrand Canada, 2012).
- 1859, the Banque Nationale initiated operations in Lower Canada, merging with the Banque d’Hochelaga in 1924 (National Bank Financial Group, 2013).
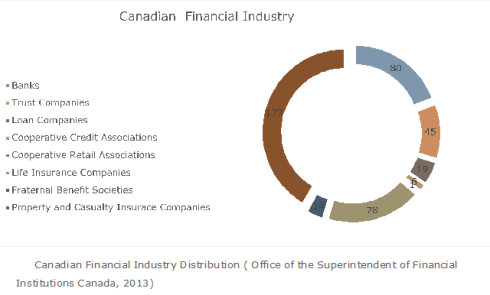
- By 2013, the Canadian financial sector had 416 institutions among Banks, Trust and Loan Companies, Cooperative Credit and Retail Associations, Life, Property and Casualty Insurances Companies and Fraternal Benefit Societies (Office of the Superintendent of Financial Institutions Canada, 2013).
BMO Financial Group, CIBC, National Bank of Canada, RBC Group, Scotiabank and TD Bank Group will dominate the Canadian market by holding over 90% of total assets. These banks are colloquially known as the big six, and have been classified by the regulators as too big to fail.